Exploring AR, VR, and Wearables
Exploring AR VR Wearables can be an exciting journey into the world of immersive technology. Each of these technologies offers unique experiences and possibilities. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
1. Augmented Reality (AR)
AR enhances the user’s reality by overlaying digital information onto the real world. Devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, or heads-up displays typically facilitate this. Examples include Pokémon GO, where virtual creatures inhabit real-world locations, and AR navigation apps that provide directions overlaid on live street views.
AR has applications in various fields, including:
Education: AR can make learning more interactive by providing visualizations and simulations.
Retail: AR can be used for virtual try-ons of clothes or visualizing furniture in your home before buying.
Industrial: AR can assist workers by overlaying relevant information on machinery or providing step-by-step instructions.
Healthcare: AR can aid surgeons with real-time data during procedures or help medical students study anatomy.
2. Virtual Reality (VR)

VR creates immersive digital environments that users can interact with. It often requires a headset covering the user’s field of view and may include handheld controllers for interaction. VR transports users to different worlds, ranging from games to training simulations.
VR is used in various domains, including:
Gaming: VR gaming provides a highly immersive gaming experience where players can physically interact with the virtual world.
Training: Industries like aviation and the military use VR for realistic training simulations.
Therapy: VR is used in exposure therapy for treating phobias and PTSD.
Design: Architects and engineers use VR to visualize and modify designs before construction.
3. Wearables
 Wearable technology incorporates sensors and wireless connectivity, often worn on the body. From smartwatches to advanced devices like smart glasses, wearables serve various purposes.
Wearable technology incorporates sensors and wireless connectivity, often worn on the body. From smartwatches to advanced devices like smart glasses, wearables serve various purposes.
Wearable devices serve various purposes, including:
Health and Fitness: Wearables can track physical activity, heart rate, sleep patterns, and more.
Communication: Smartwatches allow users to receive notifications, calls, and messages on their wrists.
Navigation: Some AR glasses provide navigation information without requiring users to look at their phones.
Enhanced Experiences: Wearables can augment experiences, like using smart glasses to display additional information about objects or places.
In 2023, wearable app development prioritizes health tracking, analyzing metrics like heart rate, sleep, and stress. Apps offer personalized wellness suggestions based on data.
Health and Wellness Focus:
Wearable app development emphasizes health tracking, analyzing heart rate, sleep, and stress. Apps provide personalized wellness suggestions based on data.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration:
AR-capable wearables like smart glasses might lead to innovative apps. These apps could overlay real-time information on users’ views, enhancing navigation, assistance, and interactive experiences.
Gesture and Voice Control:
Advanced wearables may integrate gesture and voice controls for app interactions, reducing the need for physical input.
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Developers might prioritize creating apps that seamlessly work across different wearables like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and AR glasses..
Personalization and AI:
Wearable apps may use AI to analyze user data and offer personalized insights and recommendations, enhancing UX
Future Trends in AR VR Wearables in Mobile App Development
 AR Cloud Development:
AR Cloud Development:AR apps will rely on AR cloud tech for shared, persistent AR experiences, allowing interaction with AR content over time.
Wearable AR Apps:
Apps tailored to AR glasses and smart devices will offer hands-free interactions and seamless integration with surroundings
Social AR Experiences:
AR apps will use social platforms for users to share and experience AR content together in real time.
Enhanced Visual Realism:
Improved hardware will lead to more realistic and immersive AR experiences, including better tracking and lighting effects.
VR Social Platforms:
VR apps will create immersive social environments where users interact, socialize, and collaborate as avatars.
Healthcare and Therapy Applications:
Both AR and VR will be used for therapeutic purposes, harnessing their immersive potential for controlled therapeutic environments.
Training and Simulation:
VR will continue as a preferred platform for training simulations in various industries, providing safe learning environments.
Location-Based VR Entertainment:
VR arcades will create large-scale immersive experiences using location-based technologies.
Benefits of Augmented Reality (AR)
AR enhances user engagement with immersive experiences that captivate users, leading to longer session times and higher retention rates. It enables interactive experiences, provides real-world context, and visualizes products in real environments. AR also gamifies tasks, making them more engaging.
Enhanced User Engagement:
AR provides a unique and immersive experience that captivates users and keeps them engaged with the app. This can lead to longer session times and increased user retention rates.
Interactive User Experience:
AR allows users to interact with digital content in the real world, enabling a more hands-on and intuitive experience. This interactivity can make users feel more connected to the app and its content.
Real-world Context:
AR overlays digital information onto the real-world environment, providing context-rich experiences. This can be particularly valuable for navigation, education, and training apps, where real-world context is crucial.
Visualizing Products:
E-commerce apps can leverage AR to let users visualize products in their real environment before making a purchase. For example, users can see how furniture would look in their living room or how clothes would fit.
Gamification:
AR can turn ordinary tasks into interactive games. This gamification element can motivate users to engage with the app for longer periods and complete tasks they might otherwise find mundane.
Benefits of Virtual Reality (VR)
VR creates immersive experiences that engage users emotionally. It’s used in training, education, architecture, and entertainment. Hardware improvements, entertainment options, and practical applications like training and simulation make VR valuable.
Immersive Experiences:
VR creates a sense of presence and immersion that no other medium can replicate. Users feel like they are physically present in the virtual environment, leading to heightened engagement and emotional connections.
Training and Simulation:
VR is extensively used for training in industries such as aviation, healthcare, military, and more. It allows users to practice in realistic, controlled environments without real-world consequences. Surgeons, pilots, and soldiers can train in lifelike scenarios to enhance their skills and decision-making abilities.
Education and Learning:
VR provides interactive and experiential learning opportunities. Complex concepts can be visualized in 3D, making it easier for students to understand and retain information. Virtual field trips and historical reconstructions can also enhance traditional classroom learning.
Architecture and Design:
Architects and designers can use VR to create virtual walkthroughs of buildings, interior spaces, and urban planning projects. This allows clients and stakeholders to experience designs before they are constructed, leading to better-informed decisions.
Therapy and Rehabilitation:
VR is used in medical settings for pain distraction, exposure therapy, and physical rehabilitation. Patients can be immersed in calming environments or confront their fears in a controlled way.
Benefits of Wearables
Wearables track health, offer convenience, and provide real-time feedback. They monitor health, facilitate communication, and enhance experiences. Wearable tech finds uses in various industries, including healthcare, communication, and fashion.
Health and Fitness Monitoring:
Wearables like fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor metrics such as heart rate, steps taken, calories burned, sleep patterns, and more. This data helps users make informed decisions about their health and fitness routines.
Convenience:
Wearables are often lightweight and easy to wear, providing users with a hands-free experience. They can receive notifications, check messages, and perform simple tasks without needing to pull out a smartphone.
Real-time Feedback:
Wearables can provide immediate feedback on users’ activities. This can be particularly useful during workouts, helping users adjust their efforts to achieve their fitness goals.
Healthcare and Medical Monitoring:
Wearables equipped with advanced sensors can monitor medical conditions such as blood pressure, and glucose levels, and even detect irregular heart rhythms. This data can be shared with healthcare professionals for better diagnosis and treatment.
Sleep Tracking:
Many wearables can track sleep patterns, offering insights into sleep quality and duration. Users can then make adjustments to their sleep routines to improve their overall well-being.
How can businesses and developers get involved?
Businesses and developers can get involved in AR VR Wearables by following these steps:
1. Education and Research:
Stay Informed:
Stay updated on the latest trends, advancements, and use cases in AR, VR, and Wearables by following industry news, and blogs, and attending conferences.
Learn the Basics:
Familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts of AR, VR, and Wearable technologies. Understand how they work, their potential applications, and their limitations.
2. Identify Use Cases:
Business Use Cases:
Explore how these technologies can benefit your industry or business. Consider areas like marketing, customer engagement, employee training, and product development.
User Experience:
Focus on creating meaningful and engaging user experiences that leverage the unique capabilities of AR, VR, or Wearables.
3. Choose a Platform:
Select Development Tools:
Choose appropriate development platforms, software, and hardware for creating AR, VR, or Wearable applications. Major tech companies provide SDKs, APIs, and tools for developers.
Experiment:
Start with smaller projects to understand the technology and its challenges before diving into more complex applications.
4. Skill Development:
Learn AR/VR Development:
Learn programming languages and frameworks specific to AR, VR, or Wearables. Common tools include Unity for VR/AR and specific SDKs for Wearable devices.
Training and Courses:
Enroll in online courses, workshops, and tutorials dedicated to AR, VR, and wearable development to gain practical skills.
5. Collaborate and Network:
Join Communities: Participate in online forums, developer communities, and social media groups dedicated to AR, VR, and Wearables. This allows you to learn from others and share your experiences.
Attend Events: Attend industry conferences, meetups, and workshops to connect with professionals, showcase your work, and stay updated on the latest trends.
An Outlook of The Current AR/VR Market Scenario
AR is used across industries, while VR gaming thrives. VR headset technology improves, and MR gains attention. Challenges include costs, content quality, and user comfort.
 Augmented Reality (AR) Market
Augmented Reality (AR) Market
Growing Adoption:
The AR market was experiencing steady growth with applications spanning various industries including gaming, retail, healthcare, education, and more.
Mobile AR:
Mobile AR apps remained popular due to their accessibility through smartphones. Apps like Snapchat and Pokémon GO continued to demonstrate the mainstream appeal of AR.
Enterprise Adoption:
AR found significant use in enterprise applications, such as maintenance and training in industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and healthcare. Companies were using AR to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance training processes.
Smart Glasses:
There was increasing interest in AR smart glasses, with companies like Microsoft (HoloLens) and Google (Google Glass Enterprise Edition) targeting enterprise and industrial use cases.
Virtual Reality (VR) Market:
Gaming Dominance:
The VR market was primarily driven by the gaming industry. VR gaming continued to gain momentum with a growing library of titles and improved hardware.
Hardware Improvements:
VR headset technology was advancing, with higher resolution displays, better tracking systems, and more comfortable designs. This contributed to an improved overall VR experience.
Entertainment and Immersive Experiences:
Beyond gaming, VR was being used for immersive experiences like virtual tours, virtual concerts, and educational simulations.
Training and Simulation:
Industries such as aviation, healthcare, and the military were adopting VR for training and simulations, providing safe and controlled environments for practice.
Market Challenges and Trends.
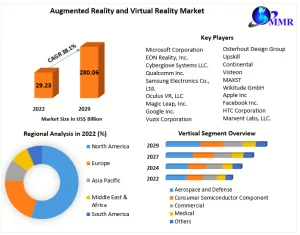 High Costs:
High Costs:
Both AR and VR faced challenges related to the cost of hardware, especially for high-quality experiences. Affordable and accessible hardware was crucial for broader adoption.
Content Quality:
The availability of high-quality, engaging content was essential for sustaining user interest in both AR and VR.
User Comfort:
VR still faces challenges related to motion sickness and discomfort, which could limit its adoption among certain users.
Mixed Reality (MR):
The convergence of AR and VR, known as Mixed Reality (MR), gained attention. MR aimed to seamlessly blend digital and physical realities, providing a more immersive experience.

















Add Comment